Incoterms are a set of international trade rules that are widely recognized and used around the world. Incoterms regulate the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in an international goods sale transaction, including related costs, risks and procedures.
Incoterms are published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) and are updated periodically. The latest version of Incoterms is Incoterms 2020.
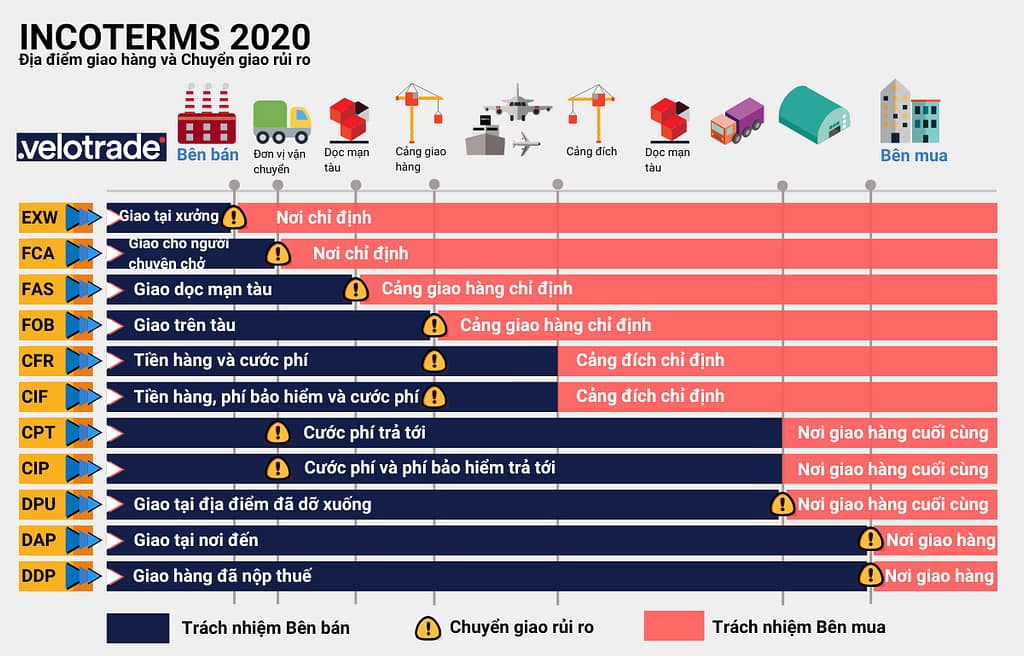
Incoterms are divided into 11 conditions, each with a different regulation on the responsibilities of the seller and the buyer. Incoterms terms are denoted by abbreviated letters, such as EXW, FCA, FAS, FOB, CFR, CIF, CPT, CIP, DAP, DAT and DDP.
Here are some of the most common Incoterms conditions:
- EXW (Ex Works): The seller delivers the goods at his premises and the buyer assumes all responsibility and risk for the goods from that point on.
- FCA (Free Carrier): The seller delivers the goods to the carrier designated by the buyer at the designated location. The seller is responsible for transporting the goods to the named location and loading them onto the means of transport.
- FAS (Free Alongside Ship): The seller delivers the goods alongside the ship at the port of loading. The seller is responsible for transporting the goods to the port of loading and unloading them overboard.
- FOB (Free On Board): The seller delivers the goods onto the ship at the loading port. The seller is responsible for transporting the goods to the port of loading and loading them on board the vessel.
- CFR (Cost and Freight): The seller bears all costs and risks involved in transporting the goods to the destination port.
- CIF (Cost, Insurance and Freight): The seller bears all costs, risks and insurance involved in transporting the goods to the destination port.
- CPT (Carriage Paid to): The seller bears all costs of transporting the goods to the designated location.
- CIP (Carriage and Insurance Paid to): The seller bears all costs, risks and insurance related to transporting the goods to the named location.
- DAP (Delivered at Place): The seller delivers the goods at the designated location and the buyer assumes all responsibility and risk for the goods from that point on.
- DAT (Delivered at Terminal): The seller delivers the goods at a designated location at the port or destination and the buyer assumes all responsibility and risk for the goods from that point on.
- DDP (Delivered, Duty Paid): The seller delivers the goods at the designated location in the importing country and the buyer bears all responsibility and risk for the goods, including import taxes.
Incoterms are a useful tool to help businesses understand their responsibilities in an international goods sale transaction. Using Incoterms properly can help businesses minimize risks and disputes.
What is the purpose of Incoterms?
- Incoterms is a set of international rules that explain the most common commercial terms in foreign trade.
- Incoterms regulate the responsibilities between the seller and the buyer in the delivery of goods, including: •Determining the location, at the point of cost division between the seller and the buyer
- Determine the location, at the point of transfer of risk between seller and buyer
- ICC is a non-governmental organization that issues the Incoterms, because Incoterms are not legally binding, they are arbitrary according to the following characteristics:
- All versions of Incoterms from 1936 to the present are still valid
- Only when the reference contract applies Incoterms will Incoterms take effect and only apply to that contract.
- Additional terms can be agreed upon within a fixed Incoterms term
- The legality of Incoterms is not higher than national laws in foreign trade.
Các điều khoản trong Incoterms?
Incoterms are divided into 4 main groups, depending on the version of Incoterms, they are further divided into smaller, more detailed conditions. But basically the groups are as follows:
- Group E: Delivery at the seller’s warehouse.
- Group F: Delivery at export port.
- Group C: Delivery at import port.
- Group D: Delivery at the buyer’s warehouse









